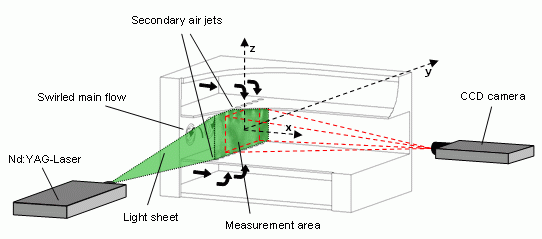
The flow field in recent RQL gas-turbine combustors can be described as the injection of secondary air jets into a swirled main flow. It is dominated by a precessing vortex helix (PVC) exiting from each swirl nozzles. In order to quantify the mixing process of both air flows PIV and concentration measurements based on Mie-scattering (QLS) have been performed inside a mixing chamber model at the TU Darmstadt, Germany. Due to the identical setup (Fig. below) of both measurement techniques which only differ in the local seeding quantities first tests images in the injection plane (x = 0) of the secondary air jets have been acquired which shall be used for both analyses.

PIV setup inside the mixing chamber model
The breakdown of the interacting PVC of all 3 swirl nozzles and the exciting secondary air jets in this measurement plane causes an unsteady 3D flow field with strong velocity gradients and very small local vortex structures. Together with the unusual seeding situation these test images require a stable and accurate PIV algorithm.
The experiments have been perfomred at the Chair of Fluid Mechanics and Aerodynamics, TU Darmstadt by M. Gnirss.
More information: http://www.sla.tu-darmstadt.de/gnirss
 |
AnaPIV - a free analysing program for PIV data |
 nambis
nambis de]
[2016-08-12]
de]
[2016-08-12]